My senior project was about specifying an application layer protocol for IoT devices. The implementation can be found here
Paper: PDF
And the following is a software architecture diagram for a Python implementation.
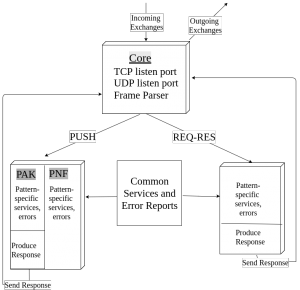
Steadily working on the prose of the survey paper. Got the feedback from Charlie and incorporating those. No major changes yet. Reading some of the failed cases of p2p/mesh mobile/wireless implementation to understand and find problems with appropriate scope.
I’m looking into different implementation of peer to peer technologies and trying to understand what and where they lack in comparison to traditional implementation. Reading about firebase API as well, which powers app like firechat.
Abstract 1
Recently I became interested in P2P messaging and/or protocols. While these protocols can offer security and prevent wiretapping (for example, bitmessaging), there are some serious drawbacks. For one, decentralization is difficult to achieve while maintaining the advantages of a centralized server, which provides major shares of benefits of client-server model. Even if decentralization is achieved, the architectures turns out to be not so well for scalability. I haven’t identified what exactly I am going to work on, but focusing on an aspect that makes the P2P protocols more robust is my motivation behind the project.
Abstract 2
It’s a widespread belief that fake news has played a noteworthy roles in shaping the voters pick for the US presidential candidate in the election cycle 2016. Fact checking, and thus weeding out fake news is one of the most difficult challenges that technology can take on; however, it’s unlikely for a set of algorithm to match the accuracy of a human fact checker, as of today. In this paper, we examine how natural language processing can help finding patterns in dubious claim as opposed to stories that are factually consistent. Employing artificial intelligence agent, we are able to show that a “true story” is supported by several sources and report the same event/fact, while a fake news story is likely reported from a single source and gets circulated. In addition to that, we’ll also examine how AI can be used to detect the extent to which a story is verifiable, which is a key characteristic of a credible story.
Abstract 3
When a device is connected to the internet, a combination of several data points uniquely identify a machine, which is known as browser fingerprinting. Advertisers and marketers use cookies in order to target potential customers, and it is very easy to abuse those tools and it leaves any device connected to the internet vulnerable to attacks. We’ll investigate the uniqueness of browser fingerprinting briefly and examine the impact of a single data point in determining the uniqueness of a fingerprint. In doing so, we’ll analyse the privacy aspect of an user and ways to achieve the security, anonymity and how the anonymity impacts the connectivity of a device.
This means that I have my WordPress page up and running. I will be posting updates on this site on my Senior Capstone project. That also made me suddenly realize my college career has begun its ending! whoops.